【20160409】Gears: Kinematic Analysis and Selection
. S M0 ~# ^4 L% O% ~$ {4 ^& @! a& `9 P
INTRODUCTION
* W) h2 H$ N1 \7 O- T" E% P9 k) s! K! }: R! s+ p
In general, the function of a gear is to transmit motion from one rotating shaft to another. In addition to transmitting the motion, gears are often used to increase or reduce speed, or change the direction of motion from one shaft to the other.
* C# \- t: B. G, K. e通常来说,齿轮的功能是在一个转动轴与另一个之间传递运动。除此之外,齿轮也常用于增速或降速,或者改变两轴的运动方向。
2 e6 c, G0 E6 [) m5 p, {3 U1 B( E' C3 M* _) r$ ?! W; f
Friction rollers or disks that are also designed to transmit motion are less costly than complex gear configurations, but they may not be able to generate sufficient frictional forces and thus will slip under larger loads. To remedy the possibility of slipping, a gear is formed such that the smooth surfaces of the disks are replaced by teeth. The teeth provide a positive engagement and eliminate slipping.
K% ^: O* s8 w6 @尽管摩擦轮也可传递运动,而且比复杂的齿轮配置更加经济,但可能因摩擦力不足而导致打滑。为弥补这一缺陷,带齿齿轮取代摩擦轮成为了主流。带齿齿轮啮合更好,并能减少打滑现象。
# ^ A: g7 C: @" l% ~, R0 n
+ q# D+ K. [5 t9 X2 F jTYPES OF GEARS
7 I" D7 p; s* u3 ]. ]) |0 y: k8 O1 q0 M2 T0 b1 }
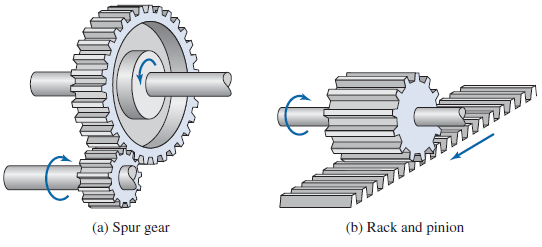
Spur gears are simplest and, hence, the most common type of gear. The teeth of a spur gear are parallel to the axis of rotation. Spur gears are used to transmit motion between parallel shafts, which encompasses the majority of applications. A pair of mating spur gears is illustrated in Figure 10.3a.
' k& f2 ]- L% d2 G b; z5 d直齿轮最简单,应用也最广。直齿轮的齿与转动轴平行(指边)。直齿轮用于传递两平行轴之间的运动,这占了实际生产中的大多数情况。图a为一对配合的直齿轮。
. B1 C ?9 T1 [& u9 f5 \3 h% y t
& N' h' L* s, q" P- I, d1 KA rack is a special case of spur gear where the teeth of the rack are not formed around a circle, but laid flat. The rack can be perceived as a spur gear with an infinitely large diameter.When the rack mates with a spur gear, translating motion is produced. A mating rack and gear are illustrated in Figure 10.3b.# L& K7 j6 z# ]% W8 @
齿条是直齿轮的特例,齿条的齿不是绕圆,而是平铺形成的。齿条可以看做是无限直径的圆。齿轮和齿条配合时产生平移运动。图b为一对配合的齿轮齿条。3 L2 M0 c8 J1 P% |. a/ ^; q
 $ t" }# k e8 T M, I6 H$ l5 l
$ t" }# k e8 T M, I6 H$ l5 l
6 |) d* q4 z0 b; `+ D5 H
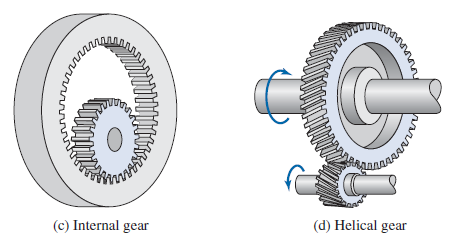
Internal or annular gears have the teeth formed on the inner surface of a circle. When mating with a spur gear, the internal gear has the advantage of reducing the distance between the gear centers for a given speed variation. An internal gear mating with a traditional spur gear is illustrated in Figure 10.3c.
& s# r3 ]" k3 t( n7 S: Q# h" f7 F内齿轮的齿在圆的内表面形成。与直齿轮啮合时,在给定的速度下,内齿轮能有效减少两齿轮中心的距离。图c为内齿轮与普通直齿轮配合。- E; v5 Q' Q8 ]* H; ~8 P4 L: s
% e! K+ ]7 G3 M# G# QHelical gears are similar to, and can be used in the same applications as, spur gears. The difference is that the teeth of a helical gear are inclined to the axis of rotation. The angle of inclination is termed the helix angle, . This angle provides a more gradual engagement of the teeth during meshing and produces less impact and noise. Because of this smoother action, helical gears are preferred in high-speed applications. However, the helix angle produces thrust forces and bending couples, which are not generated in spur gears. A pair of mating helical gears is illustrated in Figure 10.3d.
! m* b$ ^" u ?; q" ]斜齿轮与直齿轮有很多类似之处,不同的是它的齿与转轴有一定夹角,称为螺旋角。螺旋角使配合更平稳,产生的压力和噪音也更小。因此高速场合多用斜齿轮。然而螺旋角会产生轴向力与弯曲偶,直齿轮却不会产生。图d为喻队配合的斜齿轮。# I1 m' g% L& \) m( J8 A
 * P a2 `5 T7 l3 D% ?! W C' w
* P a2 `5 T7 l3 D% ?! W C' w
% T- ?9 d3 C5 p2 k1 \" S0 vHerringbone gears are used in the same applications as spur gears and helical gears. In fact, they are also referred to as double helical gears. The herringbone gear appears as two opposite-hand helical gears butted against each other. This complex configuration counterbalances the thrust force of a helical gear. A herringbone gear is shown in Figure 10.3e.
( n6 {& H. Z% n! ^ c: ` M人字齿的用途与直齿轮、斜齿轮类似。实际上也把它叫做双斜齿轮。人字齿有两个相反方向的螺线。这种复杂的配置平衡了螺旋角的轴向力。图e为人字齿。
; y1 f" e+ y$ m# q( O" P0 _+ x
* ^1 f3 _# @5 SBevel gears have teeth formed on a conical surface and are used to transmit motion between nonparallel shafts. Although most of their applications involve connecting perpendicular shafts, bevel gears can also be used in applications that require shaft angles that are both larger and smaller than 90°. As bevel gears mesh, their cones have a common apex. However, the actual cone angle of each gear depends on the gear ratio of the mating gears. Therefore, bevel gears are designed as a set, and replacing one gear to alter the gear ratio is not possible. A pair of mating bevel gears is illustrated in Figure 10.3f.
1 P" \; G9 |+ P圆锥齿轮的齿在圆锥表面上形成。用于传递不平行轴之间的运动。大多数情况下圆锥齿轮用于传递垂直轴间的运动,但也可传递成任意角度的轴之间的运动。圆锥齿轮配合时锥顶重合。然而锥角决定于齿数比。因此圆锥齿轮一般成套设计,通过改变一个齿轮来改变齿数比是不现实的。图f是一对配合的圆锥齿轮。; O- p; [! I1 N8 a- a% ]
9 `2 H. i2 z& [

$ P6 M* ?- ~# i; @! _; G, I! y0 ~3 Z3 H6 \/ r) T6 Q; x
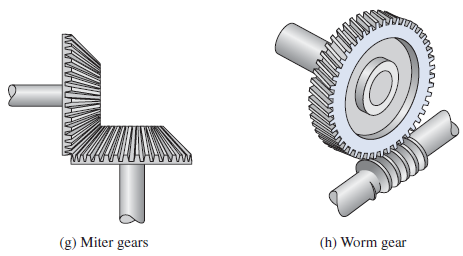
Miter gears are a special case of bevel gears where the gears are of equal size and the shaft angle is 90°. A pair of mating miter gears is illustrated in Figure 10.3g." p# L; }7 p4 Y/ v) Y9 w& {
等齿数整角锥齿轮副是圆锥齿轮的特例,两齿轮有相同的尺寸,并且两轴成90°。图g为一对配合的等齿数整角锥齿轮副。
# ]- s9 b8 y7 f8 V. d1 T, X( \+ A- @
A worm and worm gear is used to transmit motion between nonparallel and nonintersecting shafts. The worm has one tooth that is formed in a spiral around a pitch cylinder. This one tooth is also referred to as the thread because it resembles a screw thread. Similar to the helical gear, the spiral pitch of the worm generates an axial force that must be supported. In most applications, the worm drives the worm gear to produce great speed reductions. Generally, a worm gear drive is not reversible. That is, the worm gear cannot drive the worm. A mating worm and worm gear are shown in Figure 10.3h.0 ~6 [3 T# {& W, t: y8 M
蜗轮蜗杆用于传递不平行不相交轴之间的运动。蜗杆是指具有一个或几个螺旋齿,并且与蜗轮啮合而组成交错轴齿轮副的齿轮。这一螺旋齿也被称作螺纹。与斜齿轮类似,蜗杆的螺线产生轴向力。绝大多数情况下,由蜗杆驱动涡轮产生巨大的减速。一般来说涡轮驱动是不可逆的,也就是说,涡轮不能驱动蜗杆。图h为一对配合的蜗轮蜗杆。- a5 b- z% m& o* |* A
 ( @# ~9 W S+ K) [2 Y
( @# ~9 W S+ K) [2 Y
: Z& Z5 d G; C5 s9 O
|